Within the strategic blueprint of "Strengthening Primary Care" outlined at the Third Session of the 14th National People's Congress, the key to addressing weak primary healthcare resources lies in leveraging the fulcrum of medical digital transformation. As national efforts accelerate the reform of medical digitization, clinical research—a critical component in pharmaceutical innovation—is breaking through development bottlenecks with intelligent technologies, injecting new momentum into building a high-quality and efficient healthcare system.
Current clinical research faces several key challenges: First is "Data Fragmentation" – closed data management systems across research projects create collaboration barriers, requiring repeated technical integration for cross-institutional data access. Second is "Efficiency Bottlenecks" – traditional manual verification struggles with the vast data volumes of precision medicine, and "Circulation Risks" – the storage security of research data and the trustworthiness of cross-system transmission face dual challenges.
To address these challenges, a team led by Professor Lin Haotian from Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center, Sun Yat-sen University, and Professor Wong Tien Yin from Tsinghua University School of Medicine, jointly proposed an innovative clinical research data management framework based on artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain technology. This collaborative effort involved 41 experts in clinical research, AI algorithms, and blockchain technology from 15 top-tier domestic and international medical institutions and research universities.
The research findings were published online on January 25, 2025, in the top multidisciplinary journal Science Bulletin (Chinese Academy of Sciences Tier 1, Impact Factor: 21.1), in a research paper titled "An Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain technology-based data management framework for multicenter randomized controlled trials". This paper addresses issues of data integrity, objectivity, and efficiency in multicenter randomized controlled trials (RCTs). This project was successfully selected in the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology's (MIIT) "Task Unveiling" initiative for AI industry innovation and was the only award-winning project from the healthcare sector in Guangdong Province.
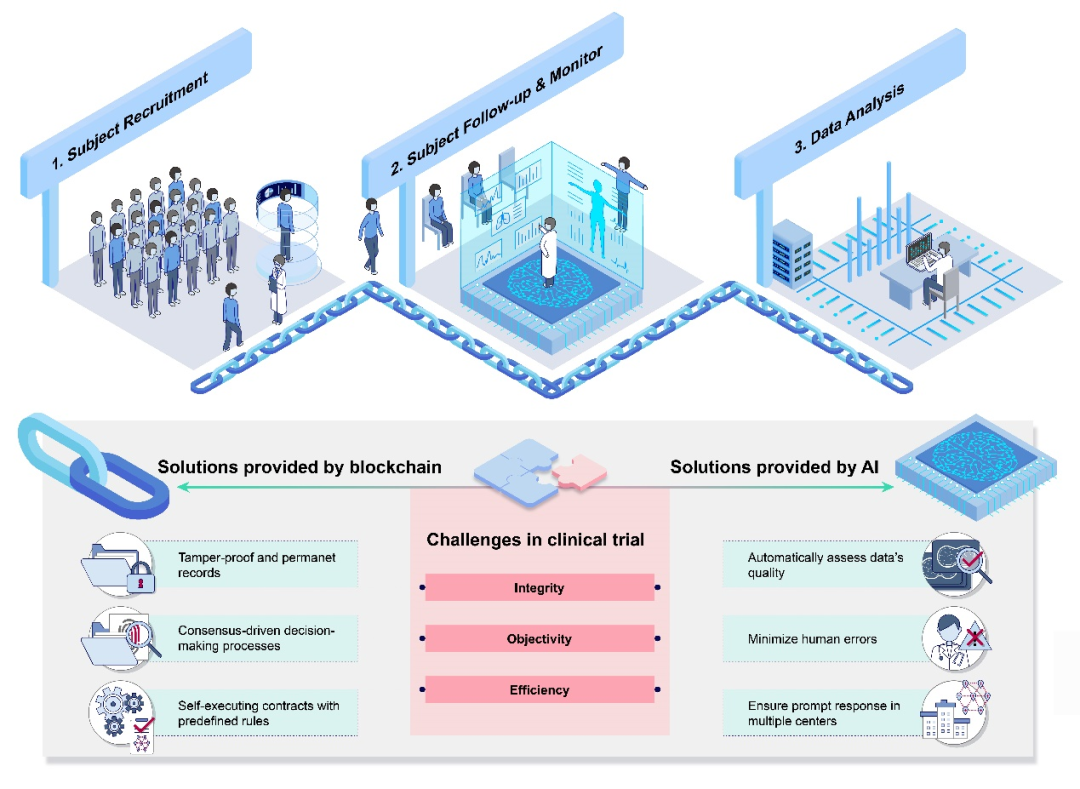
This project designed a novel data management framework for multicenter clinical trials, which has now been deployed for use in ophthalmic drug clinical trials. This framework acts like a "protective shield" for participant research data, preventing human error, resisting cyber attacks, and ensuring the authenticity and reliability of every piece of information. In the future, this technology is expected to be extended to various types of clinical trials, enabling the public to benefit from safer and more effective drugs and medical devices.
I. Blockchain: Forging an "Anti-Counterfeiting Protective Shield" for Data
Consortium blockchain technology is employed to ensure that every data modification by participants is traceable. Smart contracts are used for automated data verification and access control, ensuring only authorized users can access and modify data. Encryption using the domestic cryptographic technique SM3 adds "double layer security" for data.
II. AI: Constructing an "Intelligent Verification Gateway" for Data
The project developed two in-house AI algorithms: DeepControl and DeepGrading, for image quality control and automatic grading. DeepControl automatically assesses whether examination photos are qualified based on three dimensions: image completeness, clarity, and illumination, gatekeeping image quality (accuracy exceeds 90%). DeepGrading can precisely track disease progression (error rate below 16%).
III. Platform: Establishing an "Intelligent Hub" for Efficient Management
The research team integrated the advantages of AI and blockchain technologies to build a web-based data management application with significant efficiency advantages.
On one hand, the platform combines the capability of AI for rapid data processing with the blockchain's safeguard for participant data security. Previously, data management required relying on different systems for data quality control and security protection. Now, with this platform, these two critical tasks can be efficiently completed within the same architecture, greatly simplifying processes and improving overall workflow efficiency.
On the other hand, the platform underwent comprehensive stress testing and vulnerability testing targeting security and performance issues such as data integrity and network attack vulnerabilities. After repeated testing and improvement, the platform operates efficiently and stably even in high-load, high-risk conditions.
The platform was evaluated through an authoritative international Delphi survey. The Delphi method, utilizing multiple rounds of anonymous questionnaires, extensively collects expert opinions and facilitates consensus, largely avoiding excessive influence from groupthink or individual authority, ensuring scientific and objective results. This survey brought together 41 senior experts from various fields of clinical research, including domestic and international clinicians, research institutions, policy-making bodies, and pharmaceutical companies. They conducted four rounds of in-depth discussion focusing on key indicators such as the application's efficiency and reliability. Based on questionnaire feedback and opinion refinement, a highly consistent expert consensus was reached, fully recognizing the program's significant advantages in enhancing the efficiency and quality of clinical trial data management.
In the current era of rapid AI development, follow-up research will incorporate the latest multimodal models to address broader and more complex clinical trial scenarios. Overall, this study proposes an innovative data management framework integrating AI and blockchain technology. With its outstanding performance, it paves a new path for clinical trial data management and is expected to be widely applied in more clinical scenarios, thereby building an impregnable "Great Wall of Data" for medical researchers.
Research Team
Professor Lin Haotian's team at Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center, Sun Yat-sen University, leveraging interdisciplinary strengths from domestic and international universities and research institutions, has established an ophthalmic AI diagnosis, treatment, and clinical application system: addressing key issues of data governance and security, laying the foundation for technological innovation in intelligent diagnostics; driving breakthroughs in intelligent screening and diagnosis technology for ocular and systemic diseases based on algorithmic innovation using static and dynamic eye features; constructing a new intelligent "three-tier diagnosis and treatment" model for eye diseases, enabling multi-scenario application of ophthalmic diagnosis and treatment.
The team has presided over key supported projects of the National Natural Science Foundation of China's Major Research Plan, major disease smart diagnosis and treatment projects, etc. They have published over 200 papers in top international journals such as Nature, Nature Medicine, Science, The Lancet, The BMJ, Nature Biomedical Engineering, and The Lancet Digital Health.
The technological achievements have been widely applied in representative medical institutions across China and in countries and regions along the "Belt and Road" initiative, benefiting millions of residents and patients. They lead the innovation and development of key intelligent technologies for ophthalmic disease prevention and treatment capacity, enhancing the level of ophthalmic care.
Paper Authors
Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center of Sun Yat-sen University / the State Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology is the first affiliations of this study. Dr. (Ph.D. candidate) Yun Dongyuan (Biomedical Engineering, Medical Electronics, Sun Yat-sen University), Associate Chief Physician Wu Xiaohang, Postdoctoral Researcher Chen Xi, and Postdoctoral Researcher Yang Yahan are co-first authors. Professor Lin Haotian, Professor Wong Tien Yin (Tsinghua University), and Associate Chief Physician Wu Xiaohang are co-corresponding authors.
On the occasion of the new century of Sun Yat-sen University and the 60th anniversary of Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center, this project promotes the interdisciplinary integration of medicine and engineering, cultivates interdisciplinary talents with international vision and innovative spirit, drives the independent cultivation of young talents and technological innovation, and contributes to solving major scientific problems and serving national strategic needs.
Original article link: