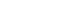Childhood and adolescence are critical periods for visual development. Eye health not only impacts an individual’s learning and quality of life in the future, but also directly influences their lifelong capacity for social participation and developmental potential. To actively support the Healthy China strategy and substantially improve eye health among children and adolescents in grassroots areas, the "Comprehensive Eye Health Project for grassroots Children and Adolescents in China" was officially launched in November 2023.
The project is jointly launched and implemented by Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center of Sun Yat-sen University, Orbis International, and Shanghai Xin’ao Brightness Foundation. It aims to establish sustainable grassroots pediatric eye care service models across five counties in Guangdong and Yunnan provinces. Focusing on the 0-18 age group in grassroots regions, the project explores replicable service models by enhancing the diagnostic and treatment capabilities of county-level hospitals, optimizing screening and referral systems, and developing standardized service protocols. This initiative advances the national eye health goal of "early screening, early diagnosis, and early treatment," safeguarding eye health while improving quality of life and social development potential for grassroots youth.
1. Full Coverage, Digital Screening
From April to May 2025, the project achieved a phased breakthrough in Fengqing County, Yunnan. Beyond routine vision and computerized refraction tests, Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center leveraged its self-developed mobile-based eye position screening system. Partnering with Fengqing County People’s Hospital, the team screened nearly 20,000 children and adolescents aged 3–18 for strabismus across 23 kindergartens, primary and secondary schools in just 22 working days—setting a new county-level record for the scale single-disease screening.
This screening fully embraced a "digital intelligence" approach. Using a "smartphone + standardized testing" model, it achieved lightweight screening equipment, standardized workflows, and intelligent data processing. The project adopted a "non-specialist volunteers + AI-powered standardized operation" mechanism: through voice-guided smartphone apps and concise training, even non-professionals can perform high-quality screenings, quadrupling efficiency over traditional manual methods. This model effectively overcomes rural challenges of "limited specialists and equipment," bringing eye care services directly to village schools.
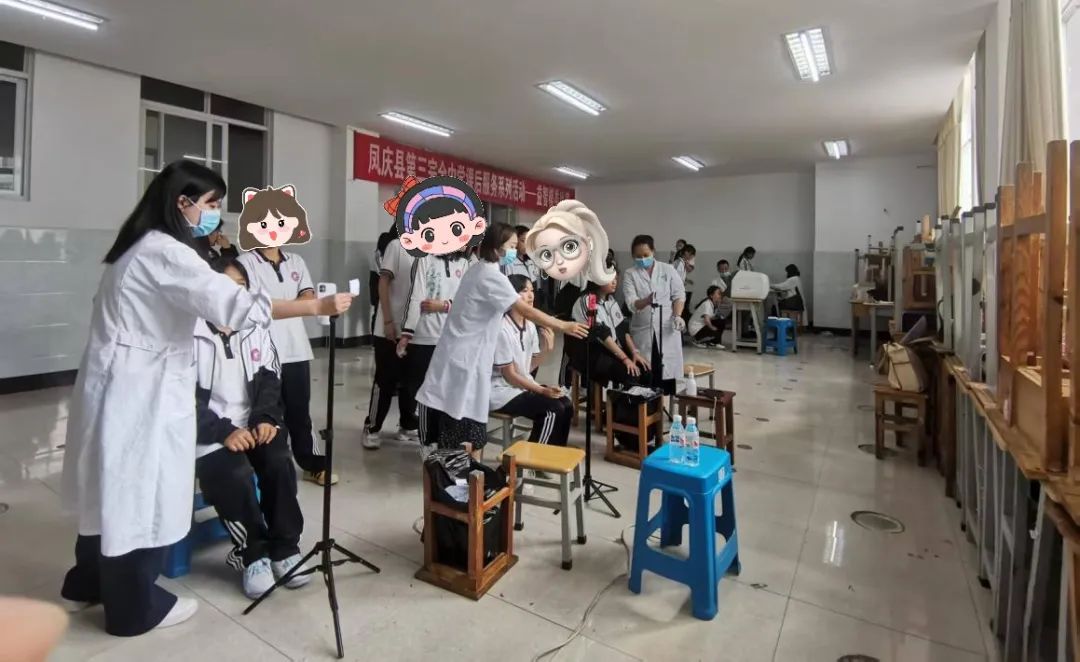
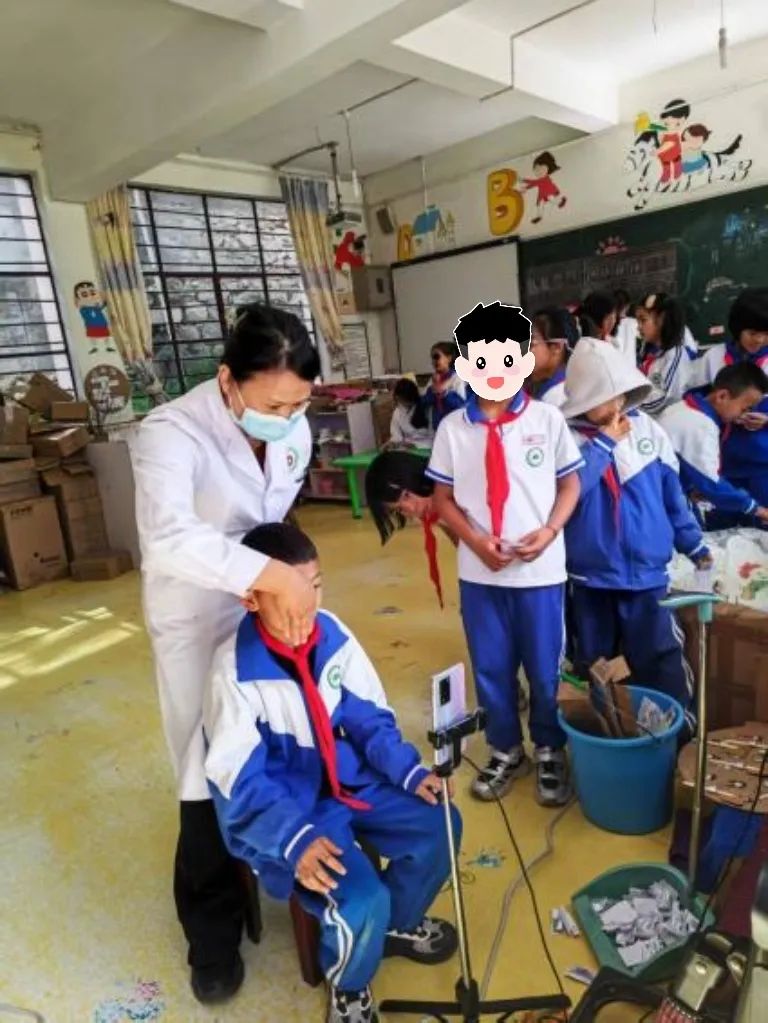



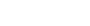
Smartphone-based standardized strabismus screening for school students—an innovative highlight of the project
2. AI Empowerment, Standardized Implementation
While achieving high coverage, the Fengqing screening practice has also ensured scientific data processing and professional results. The "Digital Ruler Intelligent Measurement System," co-developed by Tsinghua University and Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center, features automatic calculation of strabismus angles and intelligent identification of abnormal eye positions, with a screening accuracy rate of over 90%. The project has simultaneously established remote diagnosis and treatment pathways: positive cases are directly transmitted to the teleconsultation platform via encrypted channels, where the strabismus and amblyopia specialist team completes image reading and reporting through the "AI pre-screening + expert review" dual-diagnosis mechanism. It is expected to screen out approximately 500 strabismus children in need of further referral. Meanwhile, Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center continuously provides surgical support and professional training to grassroots levels, further consolidating the strabismus diagnosis and treatment capacity of county-level hospitals and building a sustainable technical support system.
3. Capacity Building, Sustainable Development
The project adheres to the concept of prioritizing both "mechanism establishment" and "capacity strengthening," advancing the development of primary-level service systems through the model of "technology deployment at the grassroots level + system optimization." On one hand, it supports the full digitalization of Fengqing County’s pediatric eye health information system and refractive archives; on the other hand, it has systematically enhanced the diagnostic and treatment capabilities of primary-level doctors through remote teaching, on-site guidance, and multiple rounds of specialized training.
Meanwhile, screening results are accurately delivered to students’ parents and schools via personalized reports, realizing "feedback on results and traceable interventions." This effectively facilitates a home-school collaborative intervention model and promotes child eye health education to take root in campuses and families.

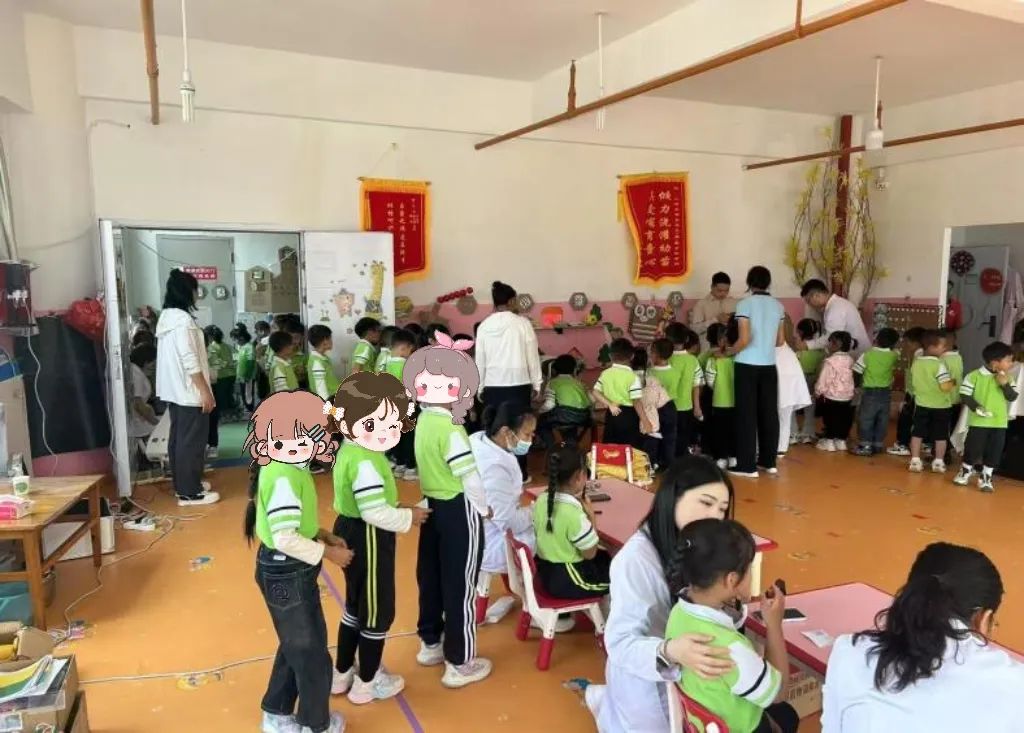
Eye health screening at Fengqing County No. 2 Kindergarten
Future Prospects: A Model for Replication
Fengqing’s screening model has not only achieved breakthroughs in technical pathways but also provided a replicable and promotable practical template for system building. This "Smart County-Level Pediatric and Adolescent Eye Health Screening Model"—based on mobile devices, AI technology, and remote collaboration—can be applied to vast grassroots areas with uneven resource allocation and weak professional capacity. It helps accelerate the formation of a multi-level, vertically connected child eye health care security network covering urban and rural areas, contributing to the achievement of the goal of "everyone enjoying basic eye health services."