Intraocular lens (IOL) decentration and tilt are significant factors affecting visual quality after cataract surgery. Highly myopic eyes face a particularly high risk of clinically significant IOL decentration (≥0.4 mm) and tilt (≥7°) following cataract surgery.
Previous results from a randomized controlled trial (RCT) by Professor Luo Lixia's team at Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center, Sun Yat-sen University, published in JAMA Ophthalmology, demonstrated that capsular tension ring (CTR) implantation in highly myopic eyes with axial length (AL) ≥30 mm significantly reduced the incidence of clinically significant IOL decentration and tilt from 29% and 26% to 3%, respectively, while also improving visual quality.
However, IOL decentration and tilt can also increase postoperative refractive prediction error. This raises the question: does CTR implantation improve refractive prediction accuracy in highly myopic eyes?
Recently, Professor Luo Lixia's team has again published findings in JAMA Ophthalmology, presenting a secondary analysis of this RCT. The study, titled “Capsular Tension Ring Implantation for Intraocular Lens Power Calculation in Highly Myopic Eyes”, employed an AL-stratified randomized controlled design. Patients were divided into three strata: 26 mm ≤ AL < 28 mm, 28 mm ≤ AL < 30 mm, and AL ≥ 30 mm. Within each stratum, patients were randomly assigned to either the control group (without CTR implantation) or the CTR group (with CTR implantation). For this secondary analysis, patients with best-corrected visual acuity <20/40 or astigmatism >3.0 diopters (D) were excluded.
The results show that CTR implantation in highly myopic eyes does not cause refractive shift, eliminating the need for additional adjustments to the target refraction. Crucially, it significantly improves the prediction accuracy of newer-generation IOL power calculation formulas specifically for eyes with AL ≥ 30 mm.
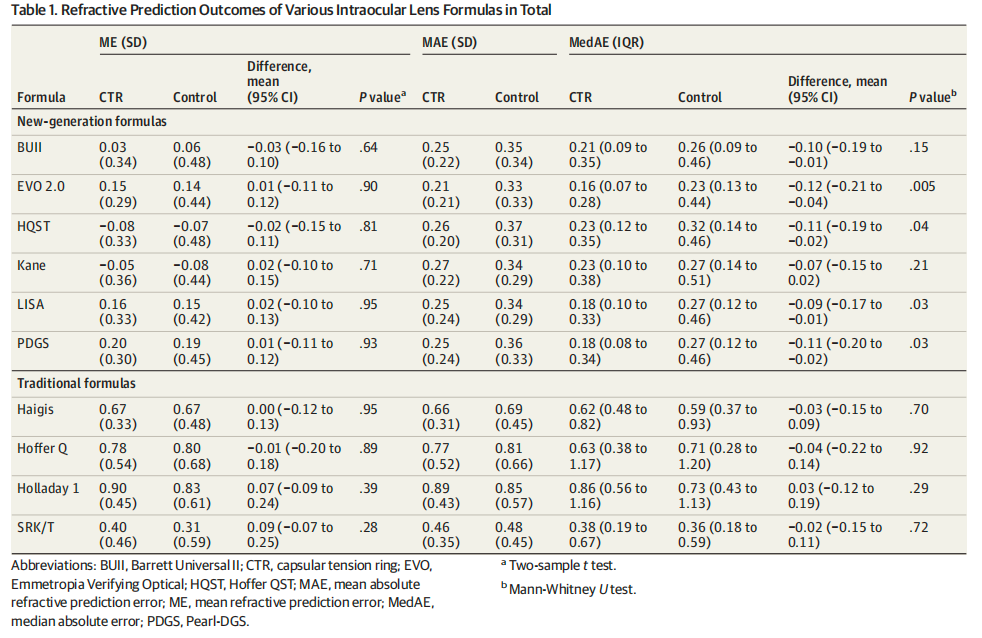
Table 1. Refractive Prediction Outcomes of Various Intraocular Lens Power Calculation Formulas
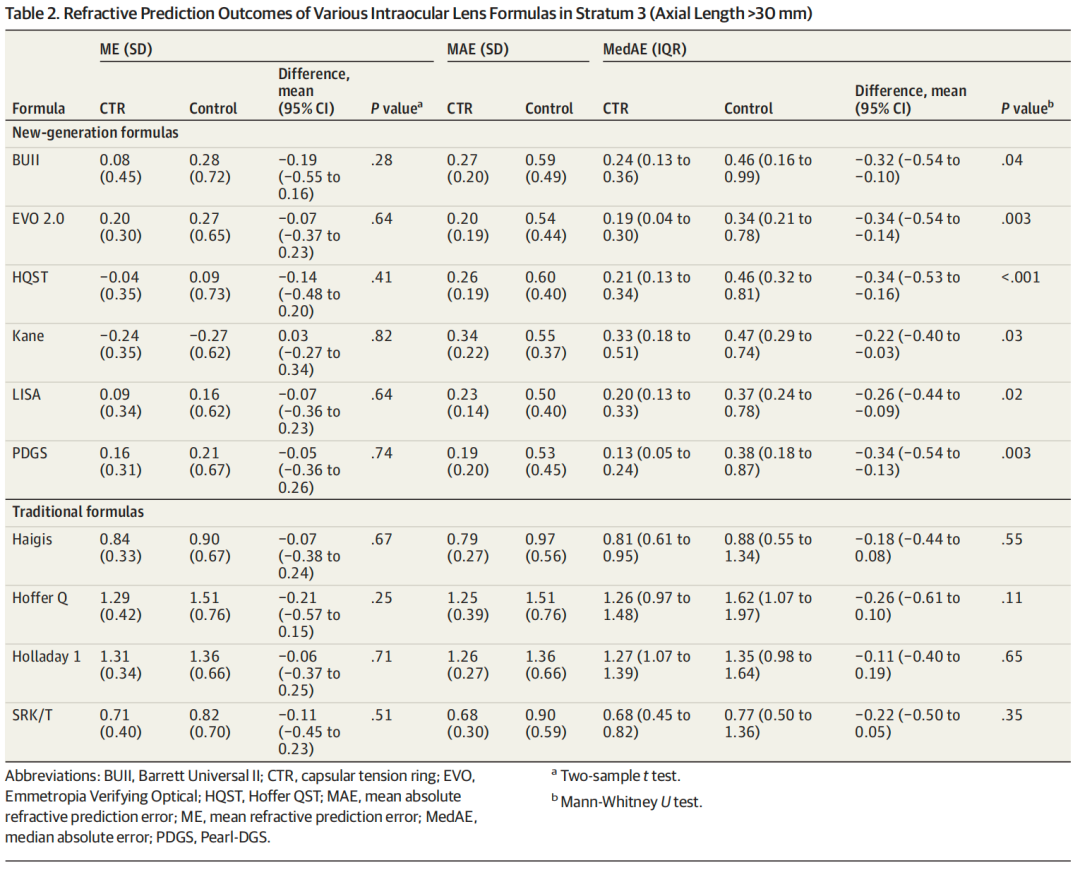
Table 2. Refractive Prediction Outcomes in eyes with AL ≥ 30 mm
This study was completed by Professor Luo Lixia's team at Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center, Sun Yat-sen University. Dr. Lin Haowen (PhD candidate), Dr. Zhang Jiaqing, and Dr. Jin Aixia (Postdoctoral Fellow, Shenzhen Eye Hospital) served as co-first authors. The corresponding authors are Professor Tan Xuhua and Professor Luo Lixia. Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center of Sun Yat-sen University / State Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology is the first and corresponding affiliation unit.
Link to Original Article:
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaophthalmology/article-abstract/2831676