On the afternoon of January 9, the 2025 Guangzhou International Medical Service Promotion Conference and the Inauguration Ceremony for the Diagnosis and Treatment Center of Major Difficult (Rare) Diseases were held at the Guangzhou Yuexiu International Conference Center. The event brought together leaders and experts from 20 diagnosis and treatment centers for major difficult (rare) diseases across 16 top-tier hospitals in Guangdong, as well as consular officials and their families from various countries stationed in Guangzhou. Discussions focused on hospital development, specialized disciplines, international exchange, and medical services for international patients. Professor Liang Lingyi, Vice President of Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center (ZOC) and Director of the Office for Prevention and Treatment of Blindness, attended the conference and delivered a keynote speech.
On November 8, 2024, the Guangzhou Municipal Health Commission issued the "Notice on Announcing the List of Guangzhou Research-Oriented Hospital (Diagnosis and Treatment Center of Major Difficult (Rare) Diseases) Projects." The application submitted by the Cataract Department of ZOC for the " Diagnosis and Treatment Center of Congenital Lens Diseases under the Guangzhou Major Difficult (Rare) Disease Project" was officially approved.
During the promotion conference, the Diagnosis and Treatment Center of Congenital Lens Diseases under the Guangzhou Major Difficult (Rare) Disease Project was invited to participate and received an official accreditation plaque.


Diagnosis and Treatment Center of Congenital Lens Diseases
As one of Guangzhou’s Diagnosis and Treatment Centers of Major Difficult (Rare) Disease, the Diagnosis and Treatment Center of Congenital Lens Diseases is established under Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center, Sun Yat-sen University—the largest public eye hospital in China (ranked first in Asia and sixth globally in the SIR University Rankings, and first among global ophthalmic institutions in the Nature Index). The center brings together renowned experts in lens diseases, refractive errors, and strabismus/amblyopia, forming a specialized team for congenital lens diseases. It adopts an innovative diagnosis and treatment model, providing one-stop services including screening, surgery, follow-up, and rehabilitation for both domestic and international patients, ensuring timely and high-quality care for complex conditions.
Leveraging the State Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology (the only one of its kind in China) and ZOC’s clinical research platform, the center is dedicated to advancing research on congenital lens diseases, promoting innovation and clinical translation of medical technologies, and striving to become a world-leading diagnosis and treatment hub for major, difficult, and rare congenital lens diseases.
Introduction to the Cataract Department
The Cataract Department treats over 5,000 patients with congenital lens diseases (including congenital cataracts and congenital lens dislocation) annually and performs more than 1,000 surgeries each year. In 2023, 90.61% of its total patients were from outside Guangzhou. In 2011, the department pioneered the establishment of the "Pediatric Cataract Home," the first of its kind in China dedicated to congenital cataract diagnosis and treatment.
As one of the earliest centers in China to perform minimally invasive phacoemulsification cataract surgery and one of the largest public hospital-based cataract and difficult disease treatment centers, the department is committed to addressing challenges in cataract diagnosis and treatment. It has developed a phacoemulsification surgery system tailored to the Chinese population and achieved internationally leading expertise in managing complex cataracts.
Among its breakthroughs, the department pioneered the world’s first "human lens in situ regeneration technology" for treating congenital cataracts—a globally challenging eye disease. This breakthrough was published in Nature and recognized as one of the "8 Major Breakthroughs in Seven Fields of Life Sciences in 2016." The department has led over 100 research projects, including the Innovation Group Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC), the 973 Program, National Key R&D Program, and Key Projects of NSFC. Its research findings have been published in hundreds of articles in top international journals such as Nature, Science, The New England Journal of Medicine, The Lancet, Nature Medicine, and The BMJ.
The department has independently developed the world’s first Class I new drug for reversing cataracts, created the Home OCT device, designed a 5G remote micron-level intelligent integrated surgical robot, and pioneered AI-based eye disease diagnostic technologies. It has also created the world’s first intraocular lens calculation formula for post-vitrectomy cataract patients. The department has won more than 20 national and ministerial awards (including the State Scientific and Technological Progress Award), obtained dozens of domestic and international patents, and authored 10 academic books on cataracts in both Chinese and English.
At the 2025 Guangzhou International Medical Service Promotion Conference, Professor Liang Lingyi delivered a special speech on medical services, highlighting ZOC’s outstanding achievements and significant influence in ophthalmic medical care, scientific research, and international collaboration. She shared the hospital’s advanced experience in managing complex cases and providing precise, efficient ophthalmic treatments for patients worldwide. In scientific research, ZOC promotes global access to ophthalmic care through innovations such as the 5G intelligent ophthalmic mobile clinic and AI technology. In international medical cooperation, she showcased ZOC’s long-running "Bright Journey" projects in the Maldives and Pacific Island countries.
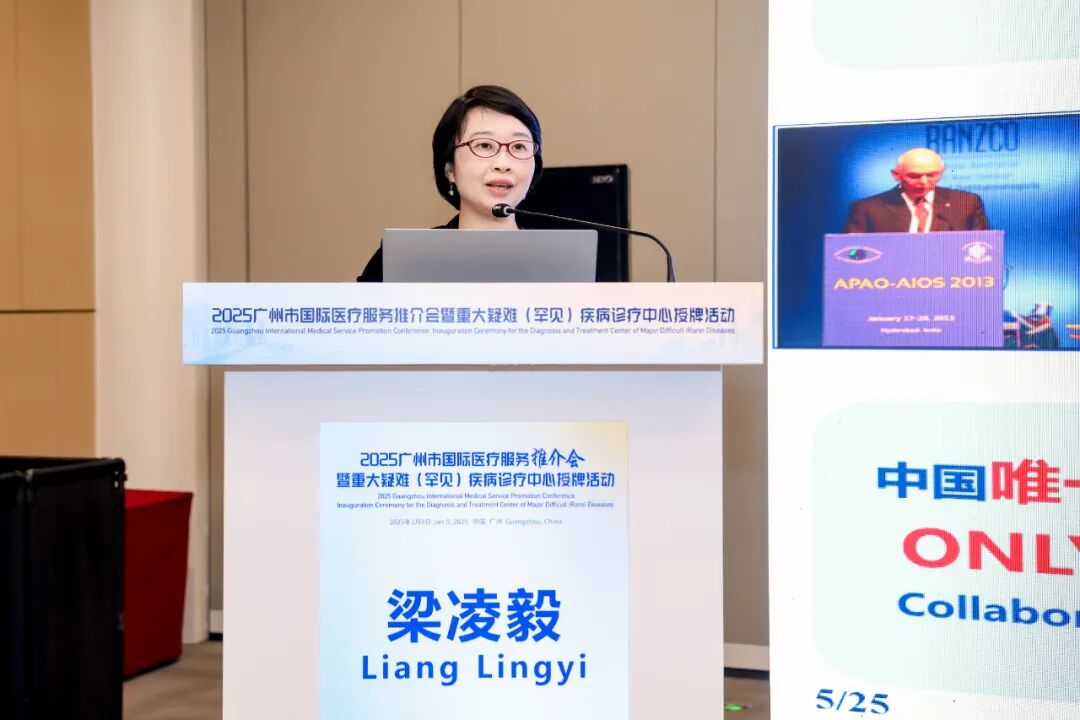

The event also featured a medical services experience session. ZOC representatives demonstrated specialized ophthalmic examinations to international guests, offered face-to-face consultations, and patiently addressed their eye health concerns. They also detailed the center’s latest achievements in ophthalmic diagnosis and treatment and its international medical cooperation projects.
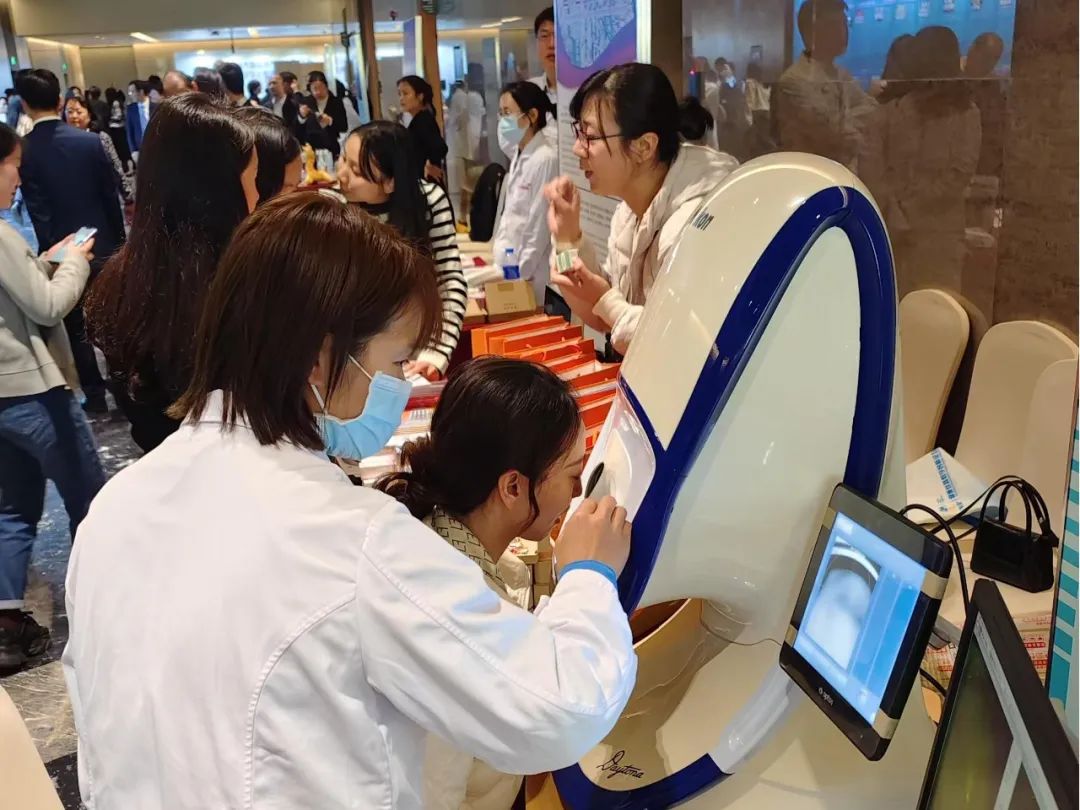

ZOC’s 5G intelligent ophthalmic mobile clinic was displayed at the conference for guests to visit, consult, and experience. Equipped with a slit lamp, fundus camera, tonometer, OCT, and autorefractor, the mobile clinic can cover over 90% of common eye diseases, providing participants with comprehensive ophthalmic examination services. It received high praise from attendees.

This event enhanced international friends’ understanding of ZOC. The center will use this platform to further expand its international medical work and contribute to the development of medical internationalization.
Taking the approval as a Guangzhou’s Diagnosis and Treatment Center of Major difficult (Rare) Disease as an opportunity, ZOC will further integrate and optimize resources across departments to improve medical resource capacity for congenital lens diseases and provide timely, high-quality diagnosis and treatment for complex conditions. It will establish consensus guidelines, introduce and share new technologies, promote homogenization and standardization of diagnosis and treatment, and build a one-stop service model for seamless screening, surgery, follow-up, and rehabilitation. By leveraging and promoting cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence, ZOC aims to achieve precision diagnosis and treatment, promote vision rehabilitation, and strive to build a world-leading diagnosis and treatment center for major, complex, and rare congenital lens diseases.